To achieve the required depth and strong foundation, we need to study the soil where the construction is going to take place. So in this post, we are going to discuss the bearing capacity of soil
Contents of the Article
show
What is the bearing capacity of Soil?
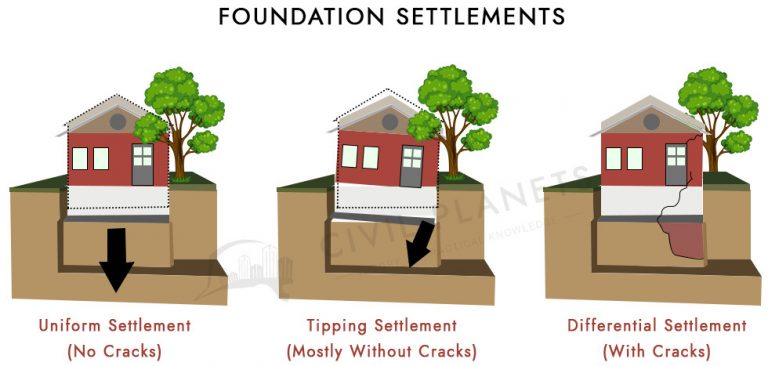
The maximum capacity of the soil that supports the structural load without any shear failure or settlement is called the bearing capacity of the soil. It is calculated in load per unit area.
Factors affecting bearing capacity
When soil is imposed by loads such as buildings, bridges, etc., it tends to deform or settle. It greatly depends on the soil properties such as
- Density of soil
- Water Content
- The angle of internal friction
- Shear strength
- Permeability
Methods of Determining Bearing Capacity of Soil
- Presumptive Analysis
- Analytical Methods
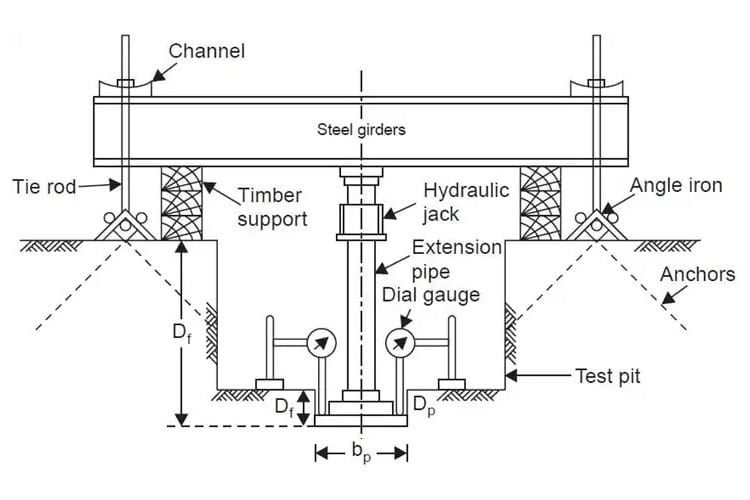
- Plate Bearing Test
- Standard Penetration Test
- Modern Testing Methods
- Centrifuge Test
Bearing Capacity Of Different Types of Soil
| # | SOIL TYPE | CAPACITY kN/m² |
| 1 | Loose Gravel | 98 |
| 2 | Fine Sand, Loose & Dry | 98 |
| 3 | Moist Clay | 147 |
| 4 | Medium Clay | 245 |
| 5 | Fine Sand & Silt | 245 |
| 6 | Soft Rock | 441 |
| 7 | Gravel Sand | 441 |
| 8 | Coarse Sand, Compact & Dry | 441 |
| 9 | Coarse Sand, Compact & Dry | 441 |
| 10 | Hard Clay | 451 |
| 11 | Residual deposits of Shatters & broken bedrock | 883 |
| 12 | Sand Stone, Lime Stone | 1618 |
| 13 | Hard rock – Granite, Dionite | 3236 |
Happy Learning 🙂