Actions or forces which cause stresses, deformations or displacements in a structure are known as Structural Loads. The forces are the result of anything such as moving people, self-weight, other natural forces (wind, thermal, earthquake, snow), etc.
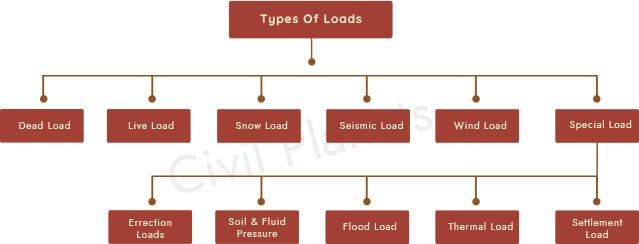
Based upon the sources of force, Types of Structural Loads will be classified as follow
- Dead Loads
- Live Loads
- Environmental Loads
- Wind Loads
- Snow loads
- Earthquake Load
- Thermal Loads
- Settlement Loads
- Special Loads
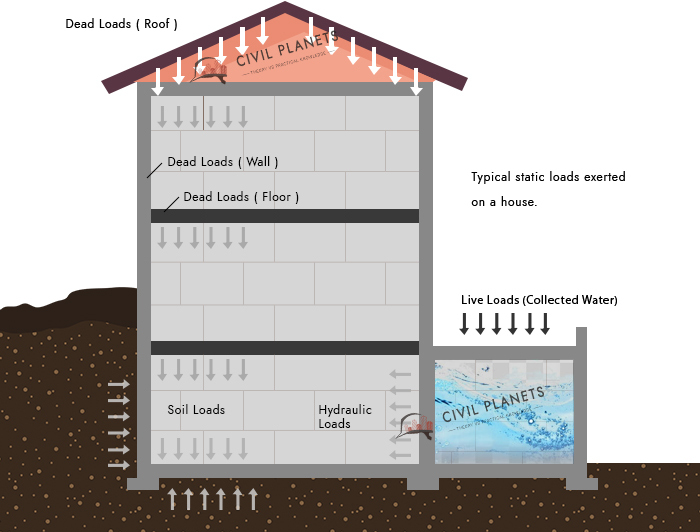
Dead Load
Dead Loads are static or permanent relatively constant over the time period of a structure.
This includes self-weight of the structural components such as walls, beams, columns, roofs, and other immovable fixed parts of the structure such as plasterboards, flooring materials, wooden frames, etc.
Dead Loads can be calculated by multiplying the unit weight of materials used and their volume.
For Example, Dead Load of 3 m3 Plain Cement Concrete = Unit weight of PCC X Volume = 24 kN / m3 X 3 m3 = 8 kN / m3
The dead loads of the different material listed below
| MATERIAL | WEIGHT kN/m³ |
| Wood | 8 KN / m3 |
| Brick Masonry | 18.8 KN / m3 |
| Plain Cement Concrete | 24 KN / m3 |
| Stone Masonry | 25 KN / m3 |
| Reinforced Cement Concrete | 25 KN / m3 |
| Steel | 78.5 KN / m3 |
| See the full list here | |
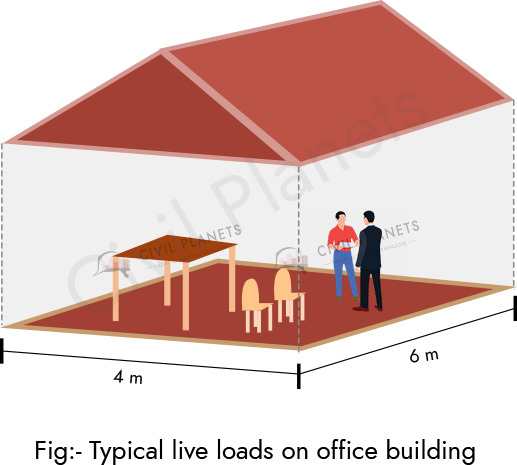
Live Loads
Live loads consists of imposed loads on the floor which are temporary, changeable, and dynamic. In simple, live loads are the loads that is not constant, but changes over time.
Some of the live loads examples are following,
- People and Furniture Items are Live loads for Residential buildings.
- Vehicles & pedestrians are live loads for bridges
- Desks & students are live loads for educational buildings
Refer the Indian Standard IS 875 (part 2) -1987 for for minimum Live Load Values.
Minimum Floor Live Loads for residential building as per IS Code
| DESCRIPTION | LIVE LOAD kN/m² |
| Floors in Residential Buildings | 2 |
| Floors in Office Buildings | 2.5 – 4 |
| Floors of Banking Hall | 3 |
| Residential Staircase & Balconies | 3 |
| Floors of Educational Buildings | 4 |
| Factory Garages (Light) | 4-5 |
| Factory Garages (Heavy) | 7.5 |
Environmental Load
Environmental Loads are caused by natural forces such as wind, snow, earthquake, and extreme temperatures.
Typical Environmental Loads are following
- Wind Loads
- Earthquake Load
- Snow load
- Thermal Loads
- Settlement Loads
Wind Loads
Pressures or stress-induced on a building by the wind blows is known as Wind Loads.
Why take wind load for consideration? Because while the wind blows it creates 3 types of loads which may cause the building to fail.
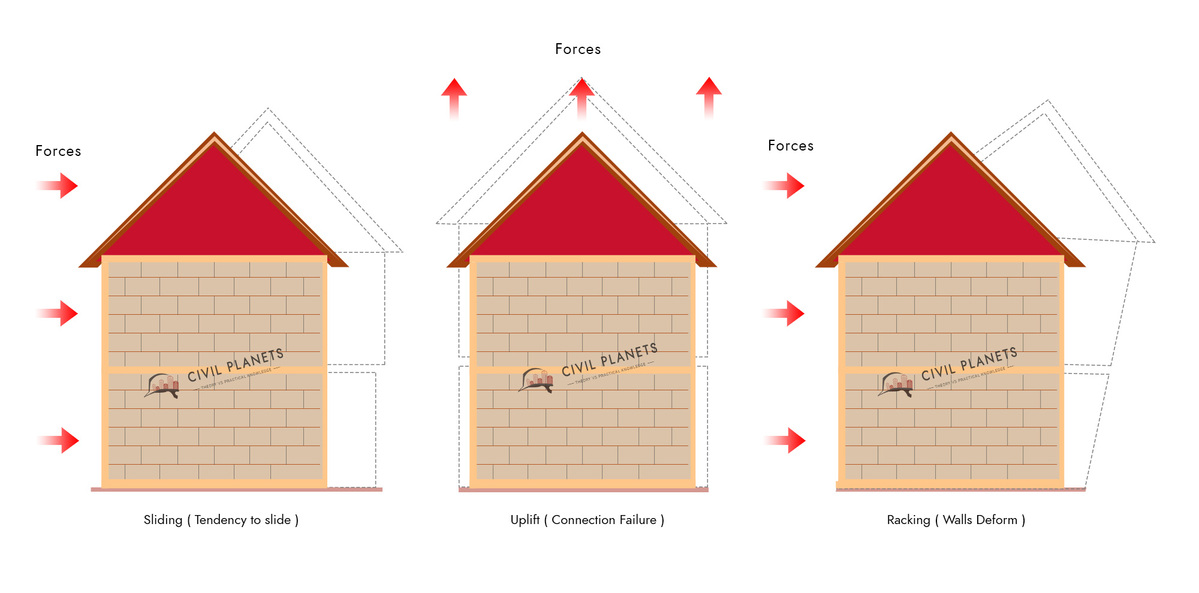
- Uplift Load – Pressures the structure to move upwards. It creates a strong uplifting force, much like a kite flying high in the air.
- Shear Load – Pressures the building over the edge to tilt, which causes walls to crack.
- Lateral Load – Pressures the building to go against the foundation and slides off.
It is not required to calculate wind loads for a small or low-level rising building. However, it should be considered in the following situations.
- High rise building
- Using lightweight material
- Using critical design shapes (especially in elevations)
- The occurrence of the hurricane in the particular region
If the structure is not enough to withstand the wind load, additional substructures or loads need to be imposed. The historical data of the locality usually determine wind load.
For more details on calculating the wind load, refer to Indian Standard Code – IS-875 (Part 3) -1987
Snow Load
Snow Loads are vertical loads that are imposed on the roof by snow during the snowfall. These loads are considered only in snowfall areas mostly in northern or mountain regions all over the world.
Snow Loads are not the result of a single action. It occurs overtime on the roof during the wintertime. Snow deposits on the roof can easily move by wind forces causing unbalanced roof loads and drifting.
That imbalance of loads on the roof causes a critical loading force on the structures.
Refer Indian Standard Code IS 875 (part 4) – 1987 for Snow Loads on the structures. Snow Load Calculator

Earthquake or Seismic Load
The load acts on the structure due to an earthquake is known as Earthquake load. Due to the ground (movement) acceleration, the building moves back and forth which causes the structure to fail.
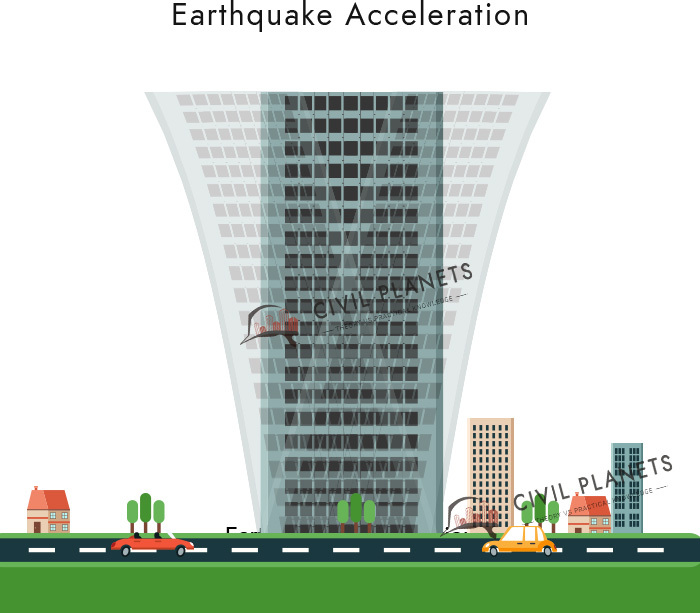
Earthquake loads are specific to the seismic region zone. The Bureau of Indian standards has published the seismic hazard mapping of India. Every country has its own set seismic zone.
According to BIS [IS-1893 (Part- 1): 2002], In India Seismic zone has been classified as four zones according to their past seismic history. Zone V is the most seismically active region, while zone II is the least.
| Zone | Intensity |
| Zone II | Low-intensity zone |
| Zone III | Moderate intensity zone |
| Zone IV | Severe intensity zone |
| Zone V | Very severe intensity zone |
Important Towns in India that have a very severe intensity zone are Bhuj, Darbhanga, Guwahati, Imphal, Jorhat, Kohima, Mandi, Sadiya, Srinagar, Tezpur. Structures in high seismic activity zones need to be carefully analyzed and designed to withstand the Earthquake loads.
Special Loads
Apart from the above 5 most common loads, the following special loads shall be taken into account if they are liable to affect the serviceability and safety as per Indian Standard Code IS 456 (2000).
- Accidental Loads arising out or human action include the following Impacts and collisions, Explosions and Fire.
- Vibration Loads such as moving machinery, heavy acceleration from cranes, hoists and the like.
- Foundation Movement / Settlement Loads occur when one part of the structure settles more than the other part of the structure. It is essential to design & study the soil conditions to avoid such settlements.
- Flood Loads – These loads are caused by floods around the foundation. It causes erosion of soil and loss of load-bearing capacity of the building.
- Soil and Fluid Pressure occur due to high water flow on the soil. It eventually affects the density of soil which creates lateral uplift force.