Choosing the right size and grade of aggregates impact the overall strength of concrete. The aggregates are taken out from the natural resources and classified into different grades. Grading of aggregates helps to identify the right aggregates for any construction works.
Advantages of Aggregates
- Available in many locations
- Low cost
- Abrasion resistance
- Easy to blend with the other concrete ingredients
- Provides strength
The aggregates are used as an important ingredient in the preparation of concrete. The fine aggregates are used in concrete as a filler material, and the coarse aggregates give the compressive strength to the concrete.

When we estimate the concrete quantity, the aggregates will occupy 70 to 75% of the volume.
The classification of aggregates depends on the grain size, density, shape, and geographical origin. So the properties of aggregates will differ based on the classification, and it may influence the mix of the concrete and strength.
The properties of aggregates that decides their nature have been listed below.
- Specific gravity
- Bulkage of aggregates
- Voids
- Composition
- Size & Shape
- Texture of Aggregate
- Porosity & Absorption
- Bulkage of aggregates
- Fineness Aggregate
- The surface area of aggregate
- Deleterious Material
- Crushing Value of Aggregate
- Impact Value of Aggregate
1. Specific Gravity
The specific gravity of aggregates is calculated by the ratio between the weight of aggregates to the weight of water which equals the aggregate weight.
The high specific gravity of aggregates contains good quality, and at the same time, low specific gravity aggregates are weak and permeable.
Normally the specific gravity value of aggregates lies between 2 to 3 which is used in construction works. The specific gravity value shows the quality and strength of the material.
2. Bulkage of aggregates
The volume of aggregates will change when it is subjected to moisture called bulkage.
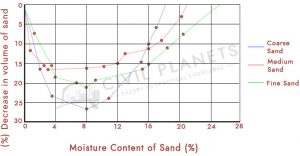
When the moisture content is present in the sand, it forms a thin film around each sand particle that makes the adjusted particles push a little away from them. This change makes the overall volume of the sand increase.
The bulking of sand is in the range between 20% to 30% and for the coarse aggregate is minimal. Bulk density is the ratio between the dry weight of the aggregates to the saturated weight of aggregates in kg/litre.
The bulk density of aggregates is dependent on the compaction and grading of aggregates in concrete.
3. Voids
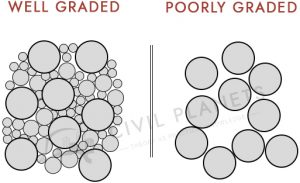
The presence of space between the aggregate particles is called voids. The saturated aggregates volume will be changed due to the presence of voids.
4. Composition
The aggregates may contain different chemical particles that react with the cement and form cracks on the concrete surface. So the aggregates must be tested to ensure that such kinds of particles are not present in the aggregates.
5. Size and Shape
The size of aggregates less than 4.75mm is called fine aggregate and beyond 4.75mm is called coarse aggregates.
The size and shape of the aggregates impact the strength and durability of the concrete. The workability of concrete might be affected when using large size aggregates.
The maximum size of aggregates must not be less than 20mm in Reinforced concrete.

Moreover, the incorrect size of aggregates such as flaky, rounded, angular, and irregular aggregates increase the voids and reduce the bondage of other ingredients in concrete. It may increase the material cost and indirectly reduce the strength of the concrete.
6. Texture of Aggregate

The surface texture represents whether the surface of the aggregates is smooth, polished, or rough. The rough surface texture is good for developing higher bondage between other ingredients of concrete which increases the strength of the concrete.
7. Porosity
We can see some tiny holes on the surface of the aggregates called pores and such kinds of rocks called porous rocks. The pores happen on aggregates due to the air bubbles formed on the surface when the molten magma solidification.
High pore aggregates may easily disintegrate when applying load.
8. Water Absorption
The coarse aggregate should not absorb water else; it may create cracks on the surface of the concrete after hardening.

The water absorption is calculated by the ratio between the dry weight of aggregate to the saturated weight of the aggregate. The water absorption will affect the water-cement ratio in concrete.
9. Fineness of Aggregate
The fineness denotes the particle size of the aggregates. Cracks may form when more fineness aggregates are used in concrete.
A high fineness value indicated the aggregate is coarser and a low fineness value indicates the aggregate is finer. The sieve analysis test founds the fineness of the aggregate.

10. Surface area of aggregate
The surface area of fine aggregate is higher than the coarse aggregate. The identification of the surface area of the aggregate is another parameter to grade the aggregate. The specific surface area is nothing but the surface area per unit weight of the aggregate.
11. Deleterious Particle
Deleterious particles affect the bondage of the concrete ingredients, thus resulting in reduced strength and durability of the concrete. The aggregates which may be used in concrete must be free from silt, clay, and other marine impurities.
12. Crushing value of aggregate
Determination of the crushing value of an aggregate is helpful to find the compressive strength of the aggregate, whether it is suitable for the concrete work or not. One of the important properties of aggregates affects the overall strength of the structure.
13. Impact value of aggregate
The aggregate impact value test is used to find the resistance capacity of aggregate from sudden impact applied on the aggregate.

14. Thermal Expansion
The aggregates should not expand due to the change of weather conditions else it may create cracks on concrete surfaces.
It is not just size and grade that affects the strength but also the properties of aggregates.
Happy Learning 🙂
