A structure built by different kinds of construction material consists of various chemical constituents.
As per IS Code, many tests would be conducted to define the quality and strength of the material involved in the construction process.
The construction material must sustain the following conditions to make the structure durable.
- It must sustain the load occurrence.
- It should not change the shape or volume due to the weather conditions.
- The material must not react with the environmental chemical.
Contents of the Article
show
Tests on Cement

The cement acts as a binding agent to bind the other ingredients of either mortar or reinforced concrete.
- Compressive Strength Test – The grade of the cement is determined by the compressive strength test of the cement after 28 days of setting.
- Soundness Test of cement – Test conducted to check the ability of cement which possesses its volume without changes after a hardened state is called a soundness test of cement.
- Initial and final setting time test – When the fresh mixed concrete or mortar takes time to become harden is called the initial setting of cement, and the completion of the hardened state is called the final setting time of cement. This test is conducted to analyze the cement’s setting time ability to withstand the construction requirements.
- Cement consistency test – The consistency of cement is the minimum water requirement to start the chemical reaction between water and cement. This test helps to identify the minimum water requirement of cement.
- Fineness Test – The fineness represents the particle size of cement. It is measured by the ratio between coarse particles (which retained in 90-micron sieve analysis) to the fineness particles (which passed through the sieve analysis).
Tests on Brick
- Compression Test on Bricks – This test is conducted to determine the compressive strength of the brick. The crushing strength of the brick should not be less than 3.5 N/Sqmm.
- Water absorption test – The bricks should not absorb more than 20% of water when immersed in water. It is calculated by the ratio between the dry weight of the brick to the weight of the saturated brick. The test ensures the quality of the bricks by wetting it for 24 hours and measuring the dry weight to its saturated brick weight.
- Soundness test – A good brick should give a clear metallic ringing sound when struck with another brick. We have discussed the whole brick quality check process.
- Shape and Size test – It is a visible test. The brick should have a straight and sharp edge. It helps to avoid the extra cost spending on cement mortar. Uneven bricks impact the width of the wall. We may need to apply extra mortar thickness to cover up the bricks to the proper thickness.
Tests on Coarse Aggregate

- Crushing Value test – The resistance capacity of aggregate under gradually applied compression load is known as aggregate crushing value. The test that is performed to measure the relative resistance is called the aggregate crushing value test.
- Impact value test – A relative measure of the resistance of aggregate due to the sudden shock or impact on it is called aggregate impact value.
- Abrasion test – The abrasion test is conducted to find the toughness of aggregate material.
- Specific Gravity test – The specific gravity of aggregates is calculated by the ratio between the weight of aggregates to the weight of water which equals the aggregate weight. The specific gravity of aggregate value lies between 2 to 3, which indicates the quality of the aggregate.
- Sieve analysis test – Helps to determine the particle size of the aggregates. Uneven aggregate particle size indirectly affects the strength of the concrete bond.
Tests on Fine Aggregate
- Silt Content Test – The silt content test is performed to determine the silt and other marine impurities in the sand, which may impact the strength of the concrete.
- Bulkage of Sand test – Helps to define the volumetric change of sand when it is saturated.
- The density of Sand Test – Helps to determine the density of sand per cubic meter, which helps in estimation.
Tests on Fresh Concrete
- U Box Test – The test used to find the filling and passing ability of freshly mixed Self-compacting concrete with the help of a U shape box is called the U box test.
- L Box Test – The test used to find the passing ability of freshly mixed self-compacting concrete in the reinforcement is known as the L box test.
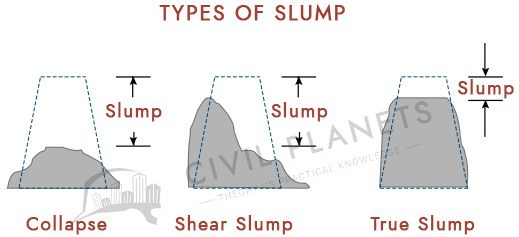
- Workability of Concrete test – The ability of concrete mixing, transportation, and placing on shuttering areas without bleeding and segregation is called the workability of concrete. It is applicable to freshly mixed concrete and conducted by different methods based on the type of concrete.
| SI | Test Name | Suitable Workability | Field/Lab |
| 1 | Slump Test | High | Field/Lab |
| 2 | Kelly Ball Test | High | Field/Lab |
| 3 | Compaction Factor | Low | Lab |
| 4 | Flow Table test | Low | Lab |
| 5 | Vee – bee test | Low & very low | Lab |
Tests on Hardened Concrete
- Non Destructive Test – Ultrasonic wave test and Rebound hammer test. Tests conducted to determine the strength of concrete without disturbing the structural integrity.
- Destructive test – Compression Testing – The actual strength of design mix concrete has been identified by this test method.
- Tensile test of concrete – To determine the flexural strength of the hardened concrete.
Tests on Soil

- Sand replacement test – The test conducted at the field to check the density of soil to ensure the proper compaction of the soil.
- Liquid limit test – To know the stiffness or softness of the soil.
- Plastic Limit Test – Test conducted to determine the moisture content required for the soil to behave as a plastic material.
Tests on Bitumen

- Flash and Fire Point Test – The flash and fire point test has been conducted to determine the safe temperature work of bitumen.
- Stripping Value test – The primary purpose of the stripping value test is to determine the presence of water molecules in adhesion between the bitumen and aggregates.
- Bitumen extraction test – The test used to determine the bitumen binder usage in the asphaltic pavement by cold dissolver method.
- Ductility test – The ductility test has been performed to determine the elongation length of bitumen at a specific temperature.
- Float test – The float test of bitumen has been conducted as per IS code 1210 to find the consistency of the bitumen.
- Penetration test – Helps to identify the grade of bitumen based on its hardness, softness, and consistency.
- Loss on heating test – The loss of heat test is conducted to find the bitumen weight loss during the heat. The presence of water molecules in the bitumen evaporates while heating and the mass of bitumen will be reduced.
- Softening point test – The softening point test is performed to determine the melting point of bitumen at a certain degree of temperature.
- Specific gravity test – The specific gravity of bitumen is in the range of 0.9 to 1.5. Determination of specific gravity for bitumen is advantageous to classify the bitumen while mixing with the aggregates on a volume basis.
- Viscosity test – The viscosity test is performed to find the fluidity of bitumen. The ability of bitumen spreading over the pavement area is known as the fluidity of bitumen.
- Water content test – Foaming occurs on bitumen when the bitumen is heated beyond the water boiling point. The dean and stark method is used to find the presence of water content in bitumen as per IS code 1211.
Tests on Steel
We know that the steel is durable against tensile force, but apart from that, many other tests are conducted to define the quality and strength of the steel.

- Tensile test of steel – To determine the ductility of the steel specimen.
- Compression Test on Steel – It is conducted to determine the compressive strength of the steel rod.
- Brinell hardness test – This test is done to determine the hardness of steel.
- Torsion Test – It is performed to assess the capacity of steel strength when twisting it against torsional forces at both ends.
Happy Learning 🙂

20 Comments
Good knowledge…
Civil lab material course suggest Pls
Good knowledge and they give clearly name of experiment and their use also
Thanks a lot for the effort, and for making the information short, simple and clear 🙏
Thankyou.
Very good knowledge
Thank you so much
Superb information in short and covered the basic all
It is really helpful
tnx you
Like to know more on LIMS in civil labs
Very helpful information….. thks to uh all
Exactly what i was looking for
I like everything about this your write-up.
It’s full of knowledge.
I need more of it in the area of water resources and public health Engineering.
So so helpful.
Good and easy synopsis for recollection
Hello sir,
I’m Rwandan,a graduate student in Highway engineering option,firstly I would like to thank you for your knowledge.
I like Geothechnical engineering so that how can i get good books of Geothechnical?
And if you don’t mind iam asking you to be my career guider in this journey
Thank you.
Faithfully yours.
Well done
absolutely amazing,thats helps for freshers student who are working as an Engineer
tensil test steel usd