We have studied in our Highway Classes during engineering that the airport layouts are constructed after considering multiple weathering facts. For example, Airport runways will be designed so that it does not exceed allowable crosswind throughout the year.
Like that, each components of an airport has a specific set of considerations. Generally, there are two types of airports. One is Towered airport and Non-Towered airport, which is a controlled or uncontrolled airport. Each airport type has more or less followed the same pattern.
Components of Airport
- Runway
- Runway lighting
- De-Icing Area
- Pre-threshold signs
- PAPI – Precision approach path indicator
- Runway Designator
- Center Line
- Touchdown zone
- Aiming Point
- Stop way
- Holding Position
- Edge Marking
- High-speed Taxiway
- Helicopter Stand
- Fire station
- Airline Service
- Bus Stop
- Taxi Stands
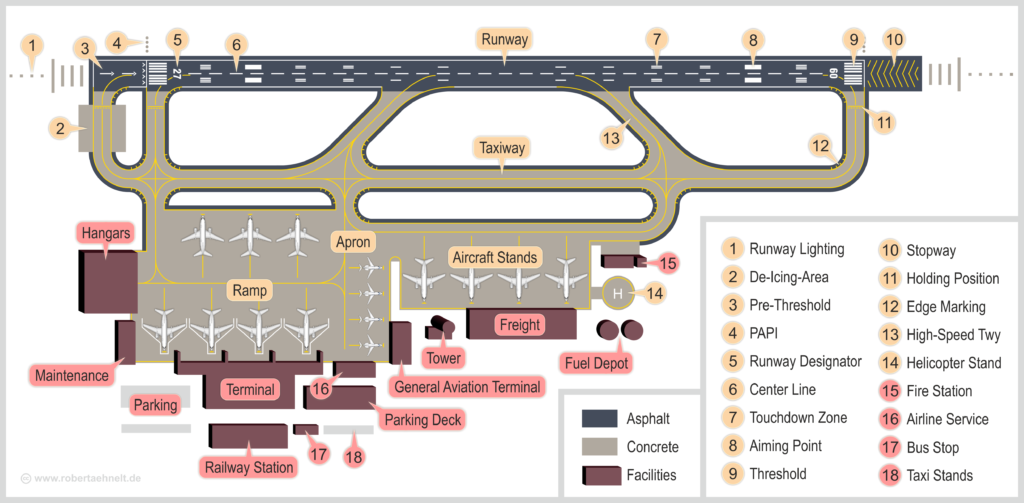
- Runway – A rectangular land area prepared in an airport for flight landing and take-off is a runway.
- De-Icing Area – The aircraft use their special deicing fluid ( a mixture of chemicals) to defrost the ice and snow from the aircraft. The deicing fluid will be heated and sprayed under pressure to remove the ice and snow.
- Pre-Threshold Area – As the name, this is the area preceding the displaced threshold (runway) suitable for aircraft to take-off but not for landing. Also Read Super Elevation

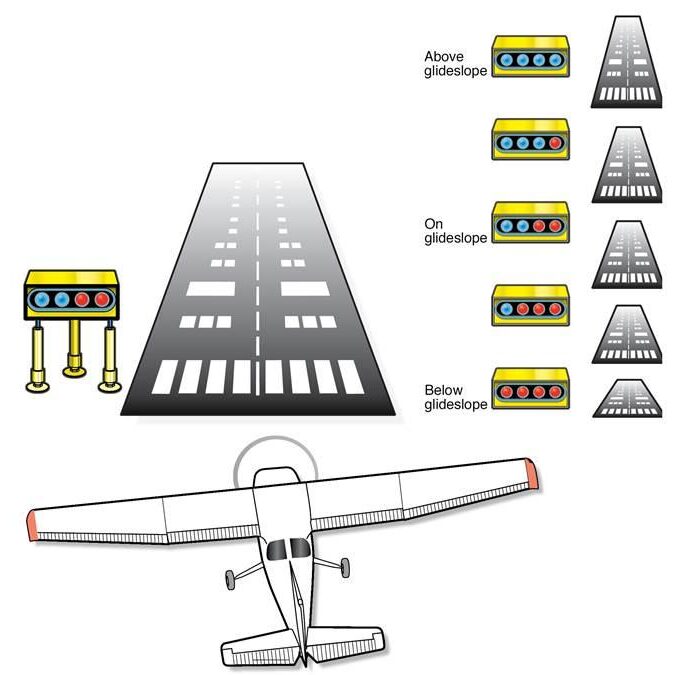
- PAPI – It is a lighting system (visual aid) that guides the pilot to maintain the right altitude to approach the runway
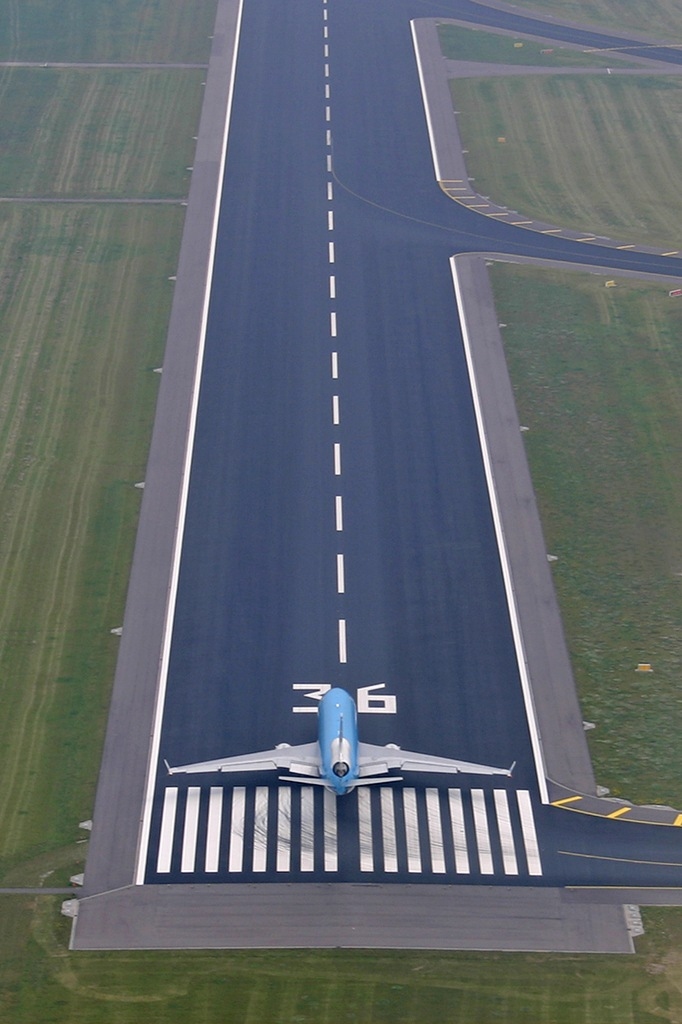
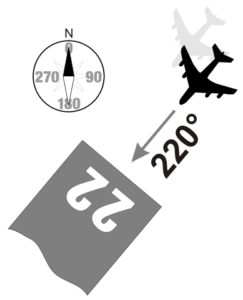
- Runway Designator – The designator represents the numbering used for taking off or landing. It consists of a two-digit number, which is the whole number nearest to 1/10th of the magnetic north when viewed from the landing direction.
- Centre Line – As the name suggests, it is the centre marking of the runway.
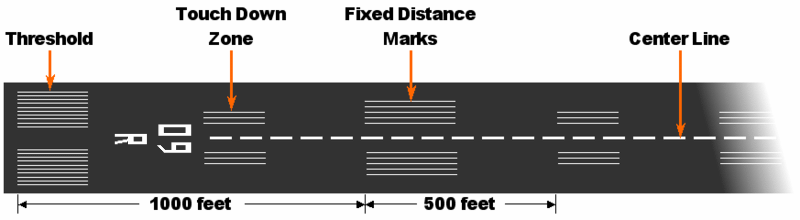
- Touchdown zone – TDZ is marked after the runway threshold. It is the intended first contact of an aircraft with the runway. Landing is not an exact science. That’s why TDZ has been provided as a safety margin where the pilot can reduce the errors before entering the actual runway.
- Aiming Point – It consists of two thick white conspicuous stripes. As the name suggests, it guides the pilot to align the aiming point with the windshield. If the point stays as the aiming point, then the pilot is maintaining the constant glide path.
- Runway Threshold – It indicates the beginning and end of the runway path available for landing and takeoff. The threshold bar will be a minimum of 10feet in width.
- Stop way – It is the area used by the aircraft when there is an event takeoff rejection.

- Holding Positions – This is more like an entrance to the runway. It denoted the Aircraft is approaching or deporting the runway.
- High-speed Taxiway – It is a long radius paved to indicate the aircraft to move at high speed from runway to centre of the taxiway.
- Helicopter Stand – As the name suggests used for helicopter landing
- Fire Station – Fire station equipped with advanced technology to prevent fire accidents at the earliest.
- Apron – Parking area for aircraft. During the parking, the aircraft will also load and unload goods. It will be more adjacent to the terminal building. The size of the aprons is designed so that it has proper drainage facilities and sufficient clearance area for the aircraft to bypass each other.
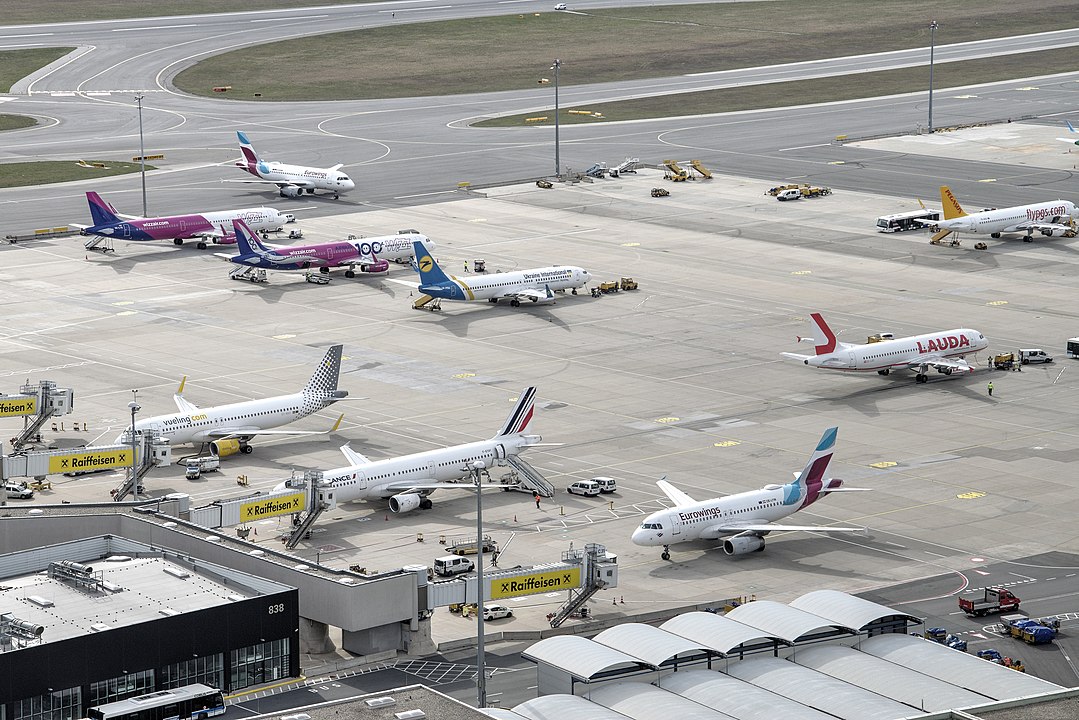

- Terminal Building – Mainly used for administration. This is the area where the passenger checking (pre & post) and waiting will take place. This is the first entrance area for the passengers into the airport.

- Control Tower – It is more like a traffic police headquarters. It observes & ensures the controlled entrance of aircraft and takeoffs. The control tower will contact the aircraft pilots during the landing and take off to avoid any possible collision. It helps the aircraft for safe landing and takeoff.

- Hangar – The aircraft repairs and servicing will take place here. It is more like a mechanic shop. It is constructed as a large shed with steel structures.
- Parking – Parking facility for the passengers to park their vehicles before entering the airport terminal building.
Happy Learning 🙂