The aggregates are inevitable materials that are mixed with other binding materials in fixed proportions to make concrete in construction.

Aggregates are the building blocks of concrete. If you calculate the required material for concrete, the fine & coarse aggregates will occupy 70 to 80% of its volume.
Origin of Aggregates
Aggregates are gained from the natural deposited rocks. Based on the mode of formation, the rocks are classified into three categories
Due to the natural geothermal activity & weathering process, the aggregates are produced from those types of rocks. Then the aggregates are involved in quality tests, whether it is safe to use in concrete or other construction activity.
Classification of Aggregates
There are so many options for the classification of aggregates,
- Grain Size
- Density
- Shape
- Geographical Origin
Let’s discuss this in detail!
Classification of aggregates based on Grain Size
Based on the grain size, the aggregates are classified into two types.
- Fine Aggregate
- Coarse Aggregate
The fine aggregates are used in concrete as a filler material to fill the voids. The coarse aggregates are used in concrete to develop the strength of the element.
The difference between the fine & coarse aggregate are listed below.
| SI | Fine Aggregates | Coarse Aggregates |
| 1 | Naturally deposited in the river bank by the disintegration of rock particles. | The crushing of disintegrated rocks manufactures Coarse Aggregates. |
| 2 | The particle size is less than 4.75mm. | The particle size is greater than 4.75mm. |
| 3 | Fine Aggregates are used in concrete as filler material to fill the voids that are formed between the coarse aggregate. | Coarse aggregates are used in concrete to produce the shape & strength for concrete. |
| 4 | Fine aggregates are used in plastering work and also a filling material. | The coarse aggregates are mainly used in concrete. |
| 5 | Increases the workability of concrete. | Decreases the workability of concrete. |
Classification of aggregates based on density
The aggregates are classified according to the density as
- Lightweight Aggregates
- Normal Weight Aggregates
- Heavy Weight Aggregates
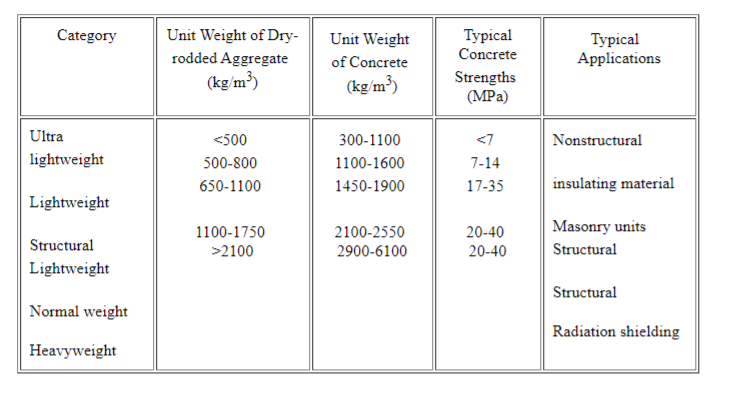
Lightweight Aggregates
The density of lightweight aggregates ranges between 800 to 1100 Kg/Cum.
The lightweight aggregates will have a high absorption value compared to other aggregates. So the slump loss happening in lightweight concrete instantly due to the absorption.
The lightweight aggregates are used as a filling material in flooring, deck slab & insulating the fireline pipes, etc.,
Normal Weight Aggregates
The normal weight aggregates are such as sand, gravel material, which we regularly use in construction.
The normal weight aggregates are used for column, beam & slab concrete. The density of normal weight aggregates in ranges between 1520 to 1680 Kg/Cum.
Heavy Weight Aggregates
The heavyweight aggregates are mostly used in construction to protect the radiation room.
The main drawback of heavyweight aggregates is it produces very low workability in concrete. The density of heavyweight aggregates range between 2100 to 2900 Kg/Cum.
Classification of aggregates based on the shape
- Rounded aggregates – You may see the rounded aggregates mostly in the seashore or riverbank area. It produces high workability & fewer voids in concrete, but mostly it was not recommended for high strength concrete elements because of its poor interlocking properties. Primarily it is used lintel concrete and also a filler material.
- Angular aggregates – The angular aggregates are low in workability. But it is mostly suitable for high
Image Credit Payment Interactive strength concrete elements because of its angularity & it produces high strength. Due to its angularity, it easily interconnects with other aggregates & fewer voids are forming in concrete.
- Irregular aggregates – The irregular aggregates will develop strength slightly lower than the angular aggregates. The irregular shapes are formed due to friction between the aggregates. The bondage between the aggregates is very low due to its irregular shape & it develops low workability in concrete.
- Elongated aggregates – In elongated aggregates, the length of the aggregates is higher than its width.
Image Credit Payment Interactive It is having low compressive strength and not recommended for concrete. If we use the elongated aggregates in concrete, the voids ratio will become high compared to the other aggregates.
- Flaky aggregates – The flaky aggregates are having a very light thickness, and it can easily crack. Due to its lower workability, it is not used in concrete, and also it quickly gets broken due to its minor thickness.
- Flaky & elongated aggregates – The flaky & elongated aggregates are having less thickness & high in length. It is also not used in concrete due to its lower compressive strength.
Classification of aggregates based on Geographical Origin
Based on the source of aggregates, it can be classified into two types, namely natural aggregates and manufactured aggregates.
Natural aggregates
The natural aggregates are available in river banks, seashore, & pits mines. The natural aggregates are used in construction work after involving some quality tests. The river sand, gravel, mud, etc., naturally available.
Manufactured Aggregates
All aggregates are developed from natural resources only. 
But the manufactured aggregates means the natural aggregates are processed to produce new size & quality aggregates which are suitable for different construction activities.
The coarse aggregates are manufactured in different sizes like 10 mm, 12 mm, 20 mm, and now manufactured sand is also available instead of river sand.
Hope you learned something valuable today. Happy Learning 🙂