The concrete that made by mixing different aggregate materials at specific ratios has different chemical particles. Various properties of concrete make it very strong and durable.
The quality of material, improper workmanship indirectly affects these properties and reduces the lifespan of the concrete. The concrete also loses its strength and durability in many ways such as
Alkali aggregate reaction is one of them where the chemical reaction happens between the aggregates, which leads the concrete to lose its strength and smooth appearance.
Alkali-Aggregate Reaction

The chemical reaction between the concrete aggregates and alkali hydroxide with the help of environmental moisture that leads to cracks on the concrete surface over a period is known as the alkali-aggregate reaction.
The appearance of crack seems like a random map, as shown in the above picture.
Alkali Hydroxides – Lithium hydroxide (LiOH), Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), Potassium hydroxide (KOH), Rubidium hydroxide (RbOH), Caesium hydroxide (CsOH)
Types of Alkali Aggregate Reaction
- Alkali silica reaction
- Alkali carbonate reaction
Alkali-silica Reaction
Silica presence in aggregates reacts with the alkali hydroxide with the help of moisture, and it forms as a gel, which induces the crack on concrete surfaces.
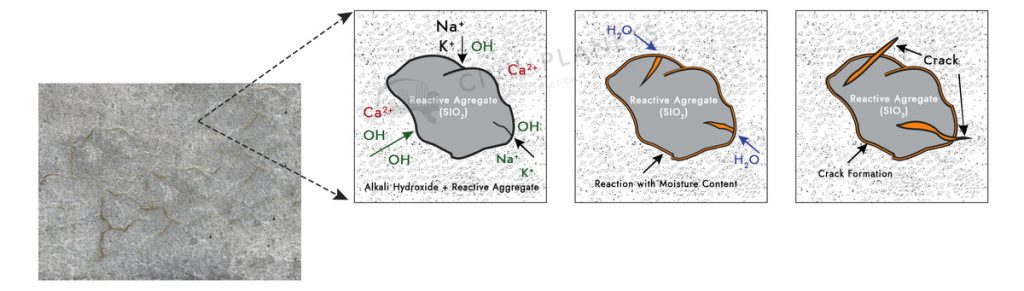
These types of crack appear mostly on the concrete surface exposed to moisture. Some soils are naturally pertaining to dampness. So it also induces the alkali-silica reaction.
Other cementitious materials such as silica fume and fly ash can control the alkali-silica reaction on concrete surfaces when mixed at a specific ratio in concrete.
Alkali-carbonate Reaction
Alkali carbonate reactions rarely happen on dolomite rocks, and it makes some sizable crack on the concrete surface.
The cementitious material cannot be controlled to reduce the cracks that happen by alkali carbonate reaction.
The possible way to prevent the cracks is not to use the aggregates, which are easily affected by the ACR. The possibilities of cracks happen by the alkali carbonate reaction is very less compared to the alkali-silica reaction.
Causes of Alkalis in Concrete
- As above said, the cement contains calcium hydroxide, which mainly causes the chemical reaction.
- The fine and coarse aggregates include some amount of silica which react with the cement.
- The water also contains a considerable amount of alkali.
- Mostly the buildings which are built near to the moisturized soil are affected by the alkali reaction.
Effects of Alkali Aggregate Reaction
- The maintenance cost will be increased.
- The concrete losses its smooth appearance and strength.
- The durability of the concrete will be reduced.
- The moisture can easily penetrate the concrete and rust the steel reinforcement.
Happy Learning 🙂



